

The interest in farming practices that maintain yield, while minimizing environmental impacts of crop production is certainly growing. These practices help a farmer to reduce the amount of external inputs, replacing them by enhanced ecosystem services. This means that instead of adding excessive amounts of fertilizers and pesticides, the capability of the agri-environment is enhanced (Bommarco, Kleijn, & Potts, 2013).
These measures affect yield only minimally, because they include measures that should be taken after the growing season on the one hand, while covering certain practices during the growing season on the other hand. The categories defined are soil related practices, catch crops and other practices.

Several measures to enhance the environment while not affecting the yield are related to soil. All of these practices take place after the growing season. They include mulching the ground, stubble and exercising no-till agriculture.

Catch and cover crops are essentially the same, although the goal of the both concepts is different. Both are plants that grow in between two main crops and both are usually not harvested. Cover crops are used to cover the soil and reduce soil erosion, while catch crops take up the excess nitrogen and thus prevent leaching. Although both have another goal, the practice is the same and they are therefore looked into together 1.

Also other practices are mentioned by policy makers. There is no great coherence in these measures, as these are neither measures that were soil related nor catch/cover crops. They include under- sowing, late mowing and limited use of mechanical equipment.
⬤ Agri-environmental schemes ⬤ Greening ⬤ Less favoured area payment
| Category | Expected from farmer | Environmental benefits | Price | Examples of regions | Barriers | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil related; mulch ⬤ | Use of mulch (plant-based) in cropping |
|
|
|
|
|
| Soil related; stubble ⬤ | Remain stubbles in field during the winter |
| 138-354 EUR/ha |
|
|
|
| Soil related; no-till ⬤ | Farmer cannot or only for a small part till soil |
|
|
|
|
|
| Catch crops ⬤ ⬤ | Cultivation of catch crops |
| 130-682 EUR/ha |
|
|
|
| Other practices; under-sowing ⬤ | Under-sowing in crops: make sure to maintain both the first and under-sowed crop are maintained |
|
|
|
|
|
| Other practices; Mowing ⬤ | Mow hard land that is hard to access Do not mow during a certain period |
| 58 EUR/ha (Romania) |
|
|
|
| Other practices; Less irrigation ⬤ | Use less irrigation |
|
|
|
|
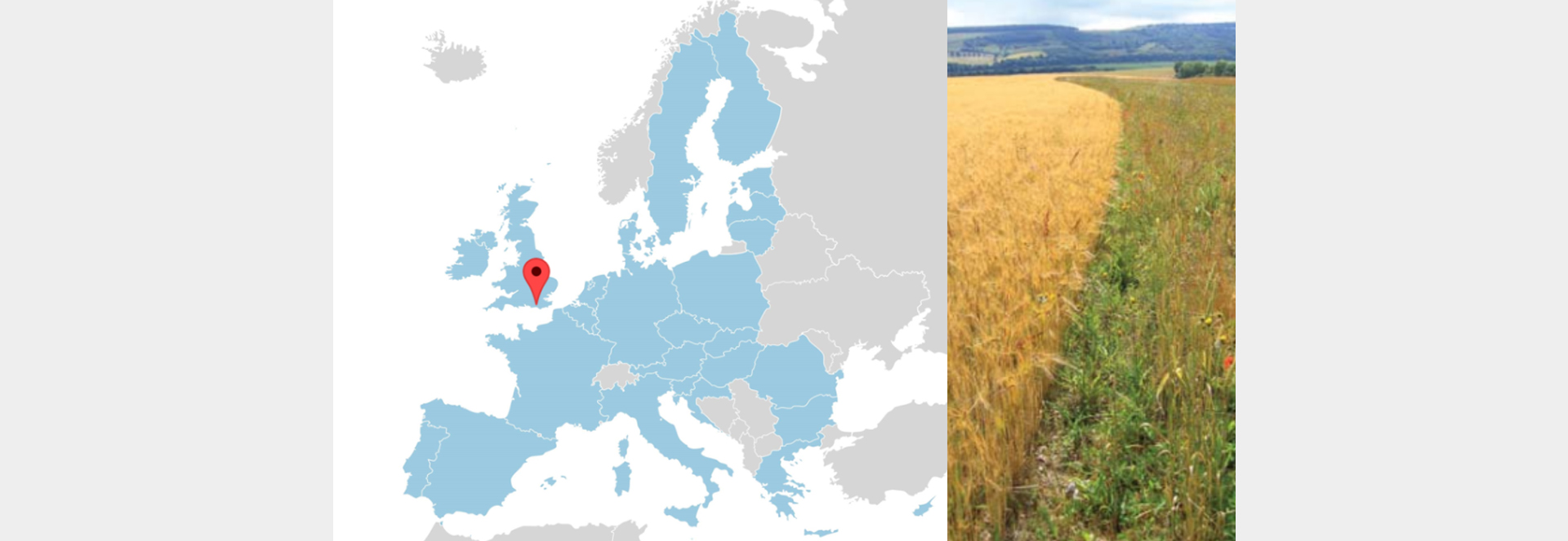
This case study covers four farms in the South of England. The farms have a mix of arable and grassland, of which some grasslands can be considered wetlands as well. All the land is managed for the greatest benefit of farmland birds. Therefore, buffer strips, over-wintered stubbles and unharvested headlands are implemented. The results of the implemented measures are incredible. Over the six years that was reported of (2003-2009) the grey partridge, corn bunting and skylarks have all grown heavily. Also mammals, wildflowers and associated insects have increased during these years. The particular case study does not mention any social and economic benefits for farmers, although these could be expected.
Source: Natural England. (2009). Farming with nature. Agri-environment schemes in action. Retrieved from http://publications.naturalengland.org.uk/publication/41005
| What: | Management of land for birds |
| Location: | West-Sussex, UK |
| Duration: | / |
| Area: | 4 farms |
| Measures taken: | Over-wintered stubbles
Buffer strips Unharvested headlands |
| Results: | More birds
More wildlife More wildflowers and associated insects |